Search Results
Viewing: 7831-7840 of 11765 | All

Specialty
Family Practice
Family Practice at Nationwide Children's Hospital is primarily composed of family physicians practicing in central Ohio who refer patients to Nationwide Children's for testing and specialty care.
Article
Mobile Care Center
The Nationwide Children’s Mobile Care Center and the Ronald McDonald Care Mobile© bring health care to your neighborhood. We have medical equipment and health care providers on board, making it easier for your child to receive care close to school or home.
Article
Diabetes and School Health
The Diabetes and School Health (DASH) Program works with school nurses to provide additional access and care for students with Type 1 diabetes.

Article
School-Based Asthma Therapy Program
Our School-Based Asthma Therapy (SBAT) Program is a link between your child's school and his or her asthma-care provider. Through the program, a child with high-risk asthma can have his or her prescribed medication administered while at school.

News
Nationwide Children’s Hospital Appoints Tim Robinson as CEO
The Board of Directors of Nationwide Children’s Hospital has announced Tim Robinson, the organization’s current executive vice president and chief financial and administrative officer, as the new chief executive officer of Nationwide Children's, effective July 1, 2019.

Article
Making a House a Home
For many people, home is a place of comfort, shelter and safety. It’s a refuge at the end of a long day and a place to build lifelong memories. But for Alma's family, home had a different meaning.

Article
Building Community Through Youth Sports and Mentorship
Learn how community outreach initiatives, like youth sports programs, are helping elementary students like Tekle.
Multimedia
How to Use a Twisthaler
Learning how to properly use a twisthaler is important to assure asthma medicine is inhaled into the airways.
Multimedia
How to Use a Nebulizer
A nebulizer is a machine used to deliver asthma medicine deep inside the lungs.
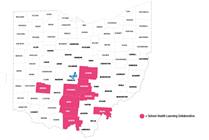
Creating a School-Based Health Model in Southern Ohio
In an effort to expand kids’ access to health care, Nationwide Children’s created the School Health Learning Collaborative, engaging and funding 13 school health teams across nine mostly Appalachian counties in southern Ohio.
