Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)

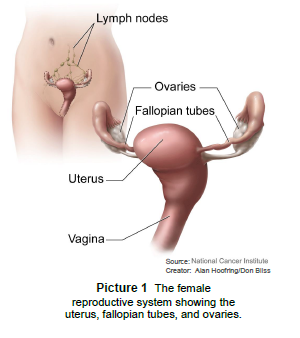
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection in the uterus, the fallopian tubes, or the ovaries (Picture 1). It is often caused by a sexually transmitted infection (STI), like chlamydia or gonorrhea. It can also be caused by vaginal infections that are not sexually transmitted.
Early medical treatment can help prevent:
- continued abdominal pain
- damage to the fallopian tubes
- This damage could cause someone born female to be sterile (unable to have children).
- infection from spreading to other parts of the body
Signs and Symptoms
Early symptoms may be:
- discharge coming from the vagina
- pain when urinating (peeing)
- lower abdomen pain
- unusual bleeding from the vagina that is not your period
Later symptoms may be:
- fever and chills
- pain when walking
- strong cramps
- pain in the abdomen (belly)
Diagnosis
To diagnose (find out if you have) PID, your health care provider will perform a pelvic exam (Picture 2).
- You will wear a hospital gown and lie on a padded table for the exam.

- Your health care provider will press on your abdomen. This is to find where the pain is coming from.
- The provider will use a metal or plastic speculum (SPEK-you-lum) to look inside your vagina. You may feel some pressure with the exam.
- They will use their hands to feel your uterus.
- If needed, samples of vaginal discharge will be taken
with a cotton swab. The swabs will be sent to the lab for more testing.
After the Exam
- Your health care provider will decide if any more tests or treatments are needed.
- If you are prescribed antibiotic medicine, take it until all of it is gone, even if you feel better.
- You may have some light spotting (bleeding) after the exam.
Preventing Future Infection
Abstinence (not having sex) is the best way to avoid PID and STIs. If you do have sex, these things might help prevent the spread of STIs:
- Limit your number of sexual partners. Know your partner(s) and their sexual history.
- Use a condom every time you have sex, the whole time you have sex.
- Have an extra condom with you in case the one you are using breaks.
- Get tested for STIs and HIV. Having an STI or HIV can increase your risk of infections.
Follow-up
If your child needs a provider, call the Nationwide Children’s Hospital Referral and Information Line at (614) 722-6200.
If you have any questions, ask your health care provider.
HH-I-62 ©1985, revised 2021, Nationwide Children’s Hospital


